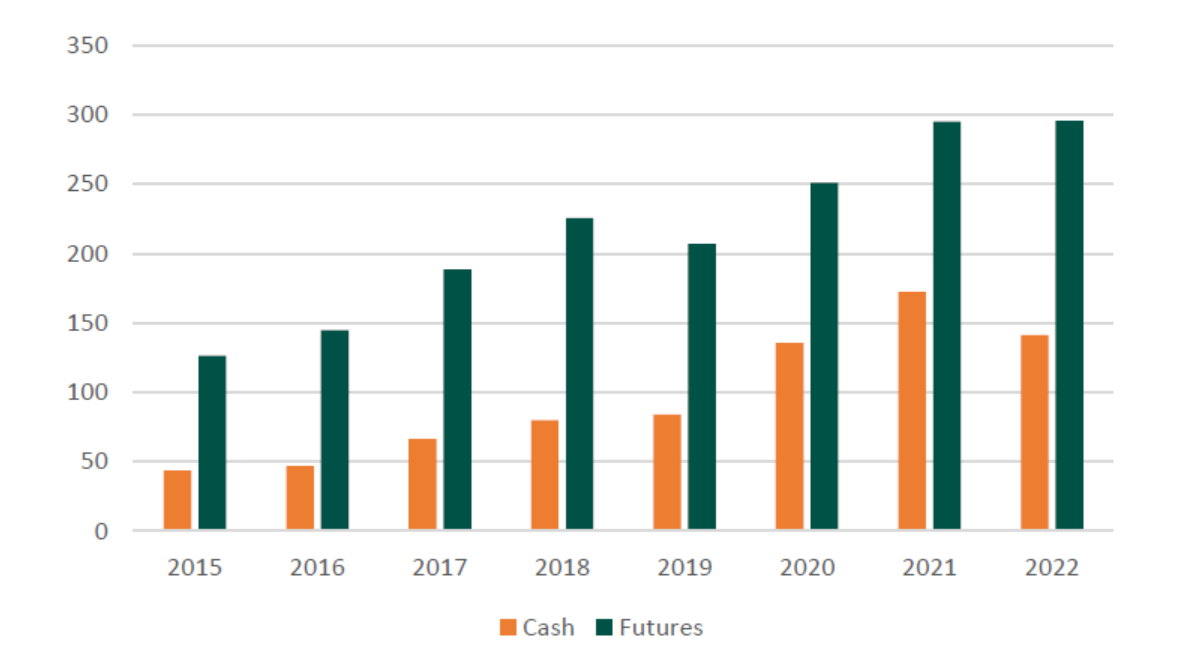
The trading volumes in India’s capital markets have seen significant growth in recent years. NSE’s Cash Equity volumes have tripled and Futures volumes have more than doubled over the last seven years.
NSE Cash and Futures Turnover (Rs Lakh Crs)
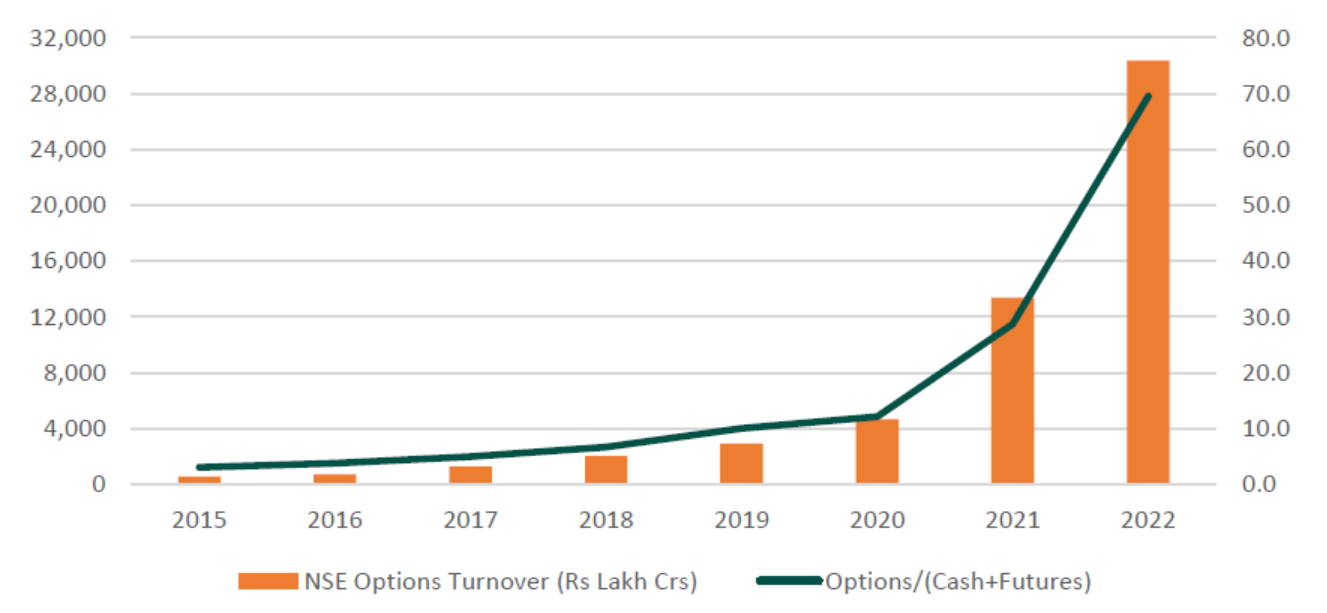
However, the growth in the cash and futures volumes seems tepid when compared to the growth in options volumes. NSE’s options turnover has increased 50x over the 2015-2022 period. Options turnover which was 3x that of the combined Cash and Futures volumes in 2015 has increased to 70x in 2022.
NSE Options Turnover (Rs Lakh Crs)
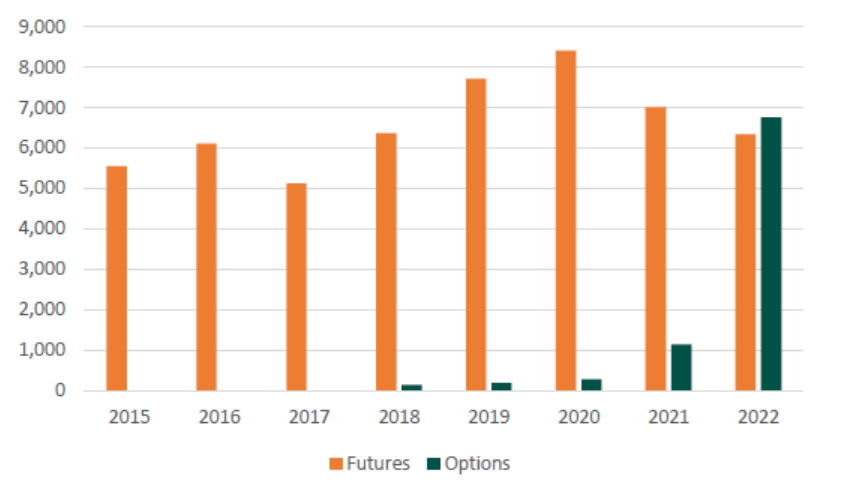
Similar trend is seen in the growth in options turnover for MCX. Over the last few years, MCX options turnover has exploded even as futures turnover has largely remained stagnant. Options, which were introduced only in 2017 by MCX, now has a higher share of turnover than futures. In December 2022, MCX options turnover was double that of the futures turnover.
MCX Futures and Options Turnover (Rs Lakh Crs)
What’s driving this unprecedented Options boom?
There are several factors that have contributed to the rise in options volumes.
- Higher market volatility: The last 3 years have seen a period of excessive market volatility in all asset classes across the globe. Option premiums increase with volatility. The higher premiums have attracted speculators looking to speculate on the direction and magnitude of price movements.
- Rise of low-cost online trading platforms: The proliferation of online trading platforms has made it easier for retail investors to access options markets and trade on their own. Brokerage firms like Robinhood and Zerodha have reduced the transaction costs and complexity of options for traders.
- Greater awareness: As options trading has become more popular, there has been a corresponding increase in the availability of information about options trading, which may have helped increase the number of people trading options. Many new investors have been attracted to online courses/webinars and YouTube videos of supposedly successful options traders hoping to quickly get rich themselves.
- Increased risk-taking behaviour (“YOLO”): The “YOLO” (You Only Live Once) attitude refers to a reckless or carefree approach to decision-making. During the Covid period, with a lot of free time at their disposal, a large number of new retail investors were using options to make sizable “all or nothing” bets. This was seen in an increase in volumes in near-expiry and out-of-money options positions, which in rare cases can result in a huge payout. The YOLO options mania was also fuelled by social media platforms like Reddit and Twitter. With lower capital requirements to trade (as compared to cash and futures), options became a preferred instrument for many retail investors.
While the above factors explain the rise of options trading globally, the rise of options in India has been far more pronounced. In mature equity markets globally, options turnover is only slightly larger than futures turnover, unlike in India where the ratio is ~100x. Even in commodity markets, the share of options turnover (<20%) globally is much lower compared to that in India.
Global Equity – F&O Turnover Mix
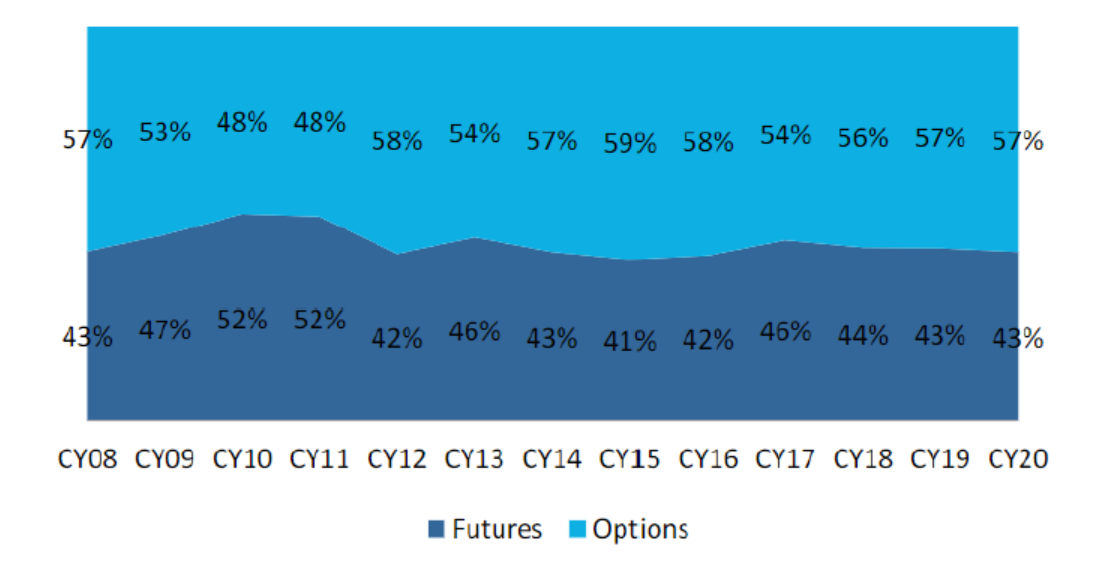
CY20 – Options as % of Total Notional Turnover
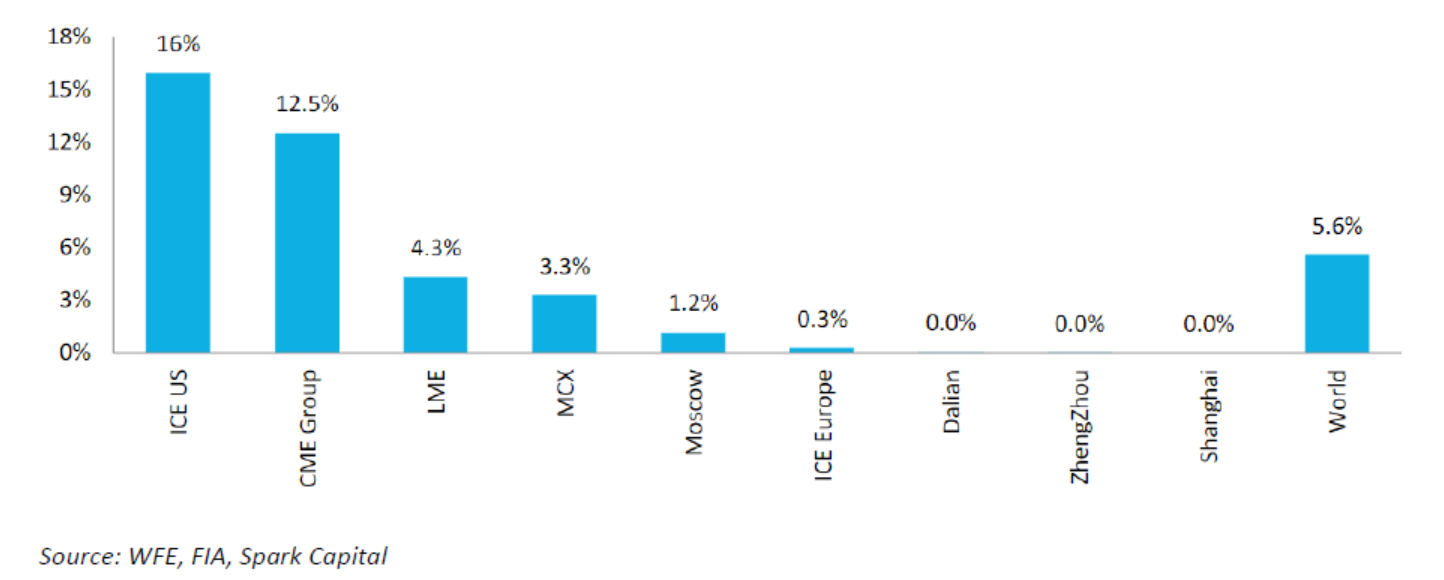
What explains the far higher share of options trading in India compared to other markets? In our view, this is largely because of local regulations that are unique to India.
- Securities Transaction Tax (STT) / Commodities Transaction Tax (CTT): India, unlike other markets, levies a tax on the value of securities traded on the equity (STT) and commodity (CTT) exchanges. This tax increases the transaction costs, making it more expensive for investors to execute trades. The impact is higher for short-term investors seeking to make small profits on a large volume of trades. STT/CTT can make several investment strategies unviable due to the higher effective costs. The amount of tax levied varies depending on the type of security being traded. For options, the tax is levied on only the option premium (and not the turnover). This along with other associated costs (brokerage, stamp duty) has resulted in options having much lower transaction costs compared to futures or cash equity. The lower transaction costs have driven many investors to use options to execute their short-term investment strategies.
- High Margin Requirements: SEBI, over the last few years, has been increasing the margin requirement for trades in the capital markets. This has been done to reduce the systemic risk from leveraged positions that can hurt market participants. Instances like negative crude prices and the sudden DHFL collapse had led to large defaults hurting brokers and could have potentially snowballed into a larger crisis. In 2020, SEBI introduced peak margin requirements, significantly increasing margin requirements. Higher margin requirements have hurt liquidity in the cash and futures market. Investors can no longer put highly leveraged trades using these securities. However, the margin requirements for options are lower than those for other instruments. Buyers of options do not have to post any margin beyond the option premium, further increasing the attractiveness of options for investors who want to use leverage.
Business Implications
The rise of options trading has significant business implications for both NSE and MCX. For NSE, options trading now accounts for ~85% of its transaction income. This number was less than 35% just five years back. This has been the biggest driver of the increase in NSE’s turnover (3.3x) and profitability (3.5x) in the last 3 years. It’s no surprise that NSE’s share price has increased from 850 in June-2020 to as high as 3500 in December-2022.
NSE Transaction Revenue Mix¹
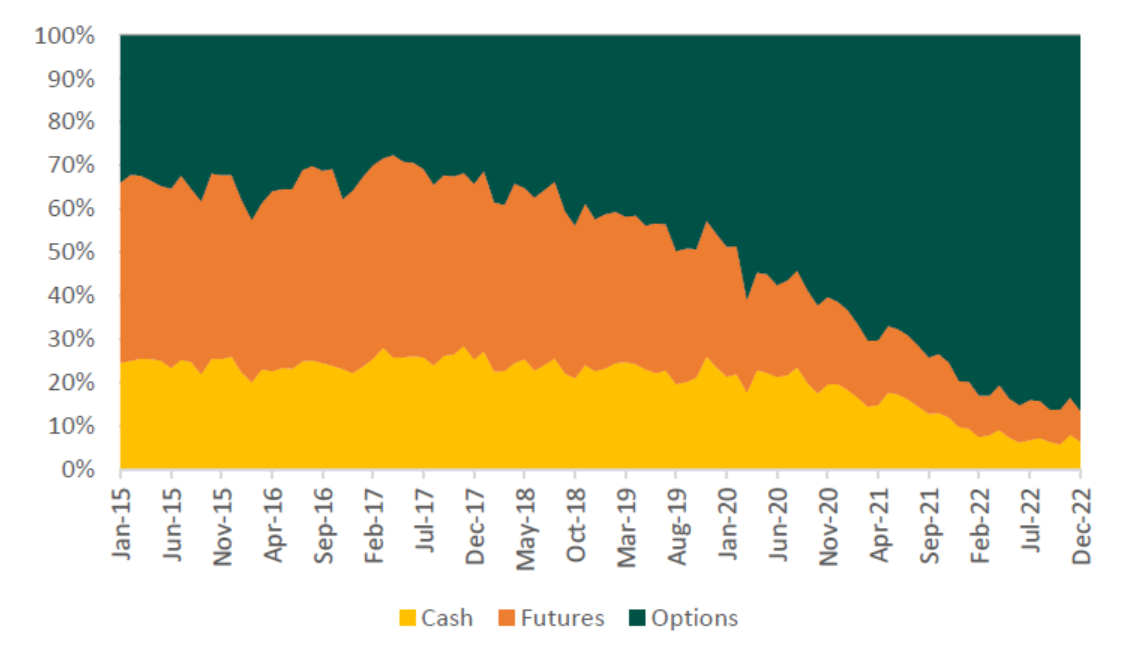
Similarly, options now account for more than 50% of the transaction income for MCX and continue to rise. In Q2 FY23, MCX reported a 53% increase in Revenue and 91% increase in PAT on a YoY basis. This was achieved despite the futures turnover declining slightly.
NSE and MCX have been key beneficiaries of the options boom in the Indian markets. MCX can further drive options growth by launching shorter-tenure products similar to NSE. While some of the factors benefitting the options market have begun to cool-down (volatility, risk-taking behaviour), the local factors (STT/CTT, peak margin) continue to sustain their growth. It is likely that the local factors will ensure that options have a much higher relevance in India compared to other markets.
Risk: SEBI has taken notice of the rapid rise in options volumes and is concerned that new investors may be taking risks that they do not fully understand. If options continue to grow rapidly, SEBI is likely to introduce new regulations that affect options volumes, possibly in the form of investor-level restrictions or options-specific margin requirements. This could have a negative impact on options volumes.
Disclaimer: All information provided is for information only and should not be considered as investment advice or a recommendation to purchase or sell any specific security. 2Point2 Capital may or may not have a position in any of the securities mentioned above.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
¹2Point2 Estimates
